
In the competitive world of business, your company’s pricing strategy can be a pivotal factor in determining its chances of success.
One effective approach is tiered pricing, which offers commensurate price points for different levels of a product or service. This strategy not only caters to a broader audience but also maximizes profit by encouraging customers to opt for higher-value tiers. It’s effective for many types of businesses, from SaaS to e-commerce.
This article will explore four clever ways to use tiered pricing to boost your business’s profitability.
What Is Tiered Pricing?
The tiered pricing strategy uses multiple price points, or tiers, for different levels of a product or service. Prices are set based on the features, duration, and quality level of each tier. This type of pricing helps businesses offer their customers multiple options without sacrificing profitability.
For example, if you offer subscription services for your business, you could create three price tiers. Tier 1 could be the basic subscription that offers a limited range of features, while Tier 2 and 3 offer additional features at higher prices.
In this way, tiered pricing helps businesses create an effective value proposition with multiple price points for different needs, helping to maximize market penetration. It also allows customers to decide which tier best fits their needs and budget without compromising on the quality of the product or service.
Four Types of Tiered Pricing Strategies
Now that you understand the basics of tiered pricing, let’s look at four different strategies that can help you implement and leverage this pricing model.
Feature-Based Pricing
Feature-based pricing is one of the most common tiered pricing methods. In this strategy, each tier offers different features at a range of price points. This type of pricing allows customers to choose from multiple options and pay only for what they need or want.
It involves creating three or more tiers based on the features included in each tier. For example, if you’re selling a product or service, you could create tiers based on the amount of features offered with each option. This allows customers to choose from multiple options and pay only for their needs or wants.
The low-price tier offers the basics of the product or service at a lower cost, while the mid and high tiers offer additional features at higher prices. This strategy allows businesses to reach a wider audience by offering specific price points for different customers.
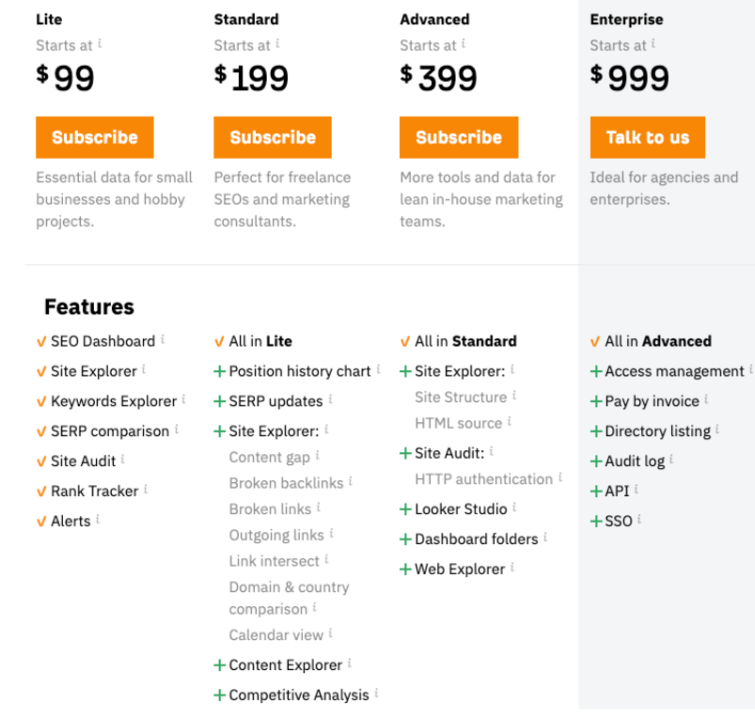
Ahrefs is an example of a business that uses feature-based pricing. They offer four subscription tiers, each with different features and prices.
Usage-Based Pricing
Usage-based pricing sets different prices depending on how the product or service is used. The price increases with usage, and customers can choose the tier that best meets their needs.
For example, if you offer software as a service (SaaS), you could create tiers based on the number of users or the required data storage. This allows customers to choose a tier that best fits their usage.
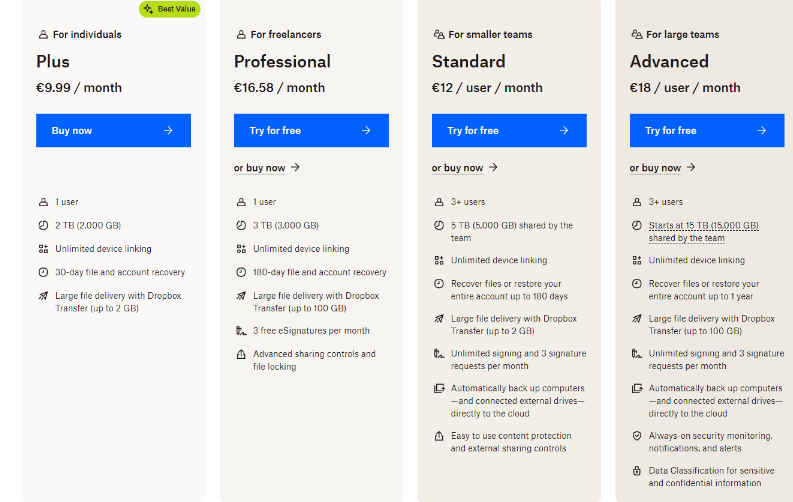
Dropbox is an example of a business that uses usage-based tiered pricing. They offer multiple tiers based on the amount of storage needed.
Duration-Based Pricing
Duration-based pricing sets different prices for subscription plans. This is similar to usage-based pricing, but it’s based on the duration of the subscription commitment rather than the amount used.
For example, if you offer a subscription service, you could create tiers based on monthly or annual commitments. This allows customers to choose a tier that fits their budget and needs best.
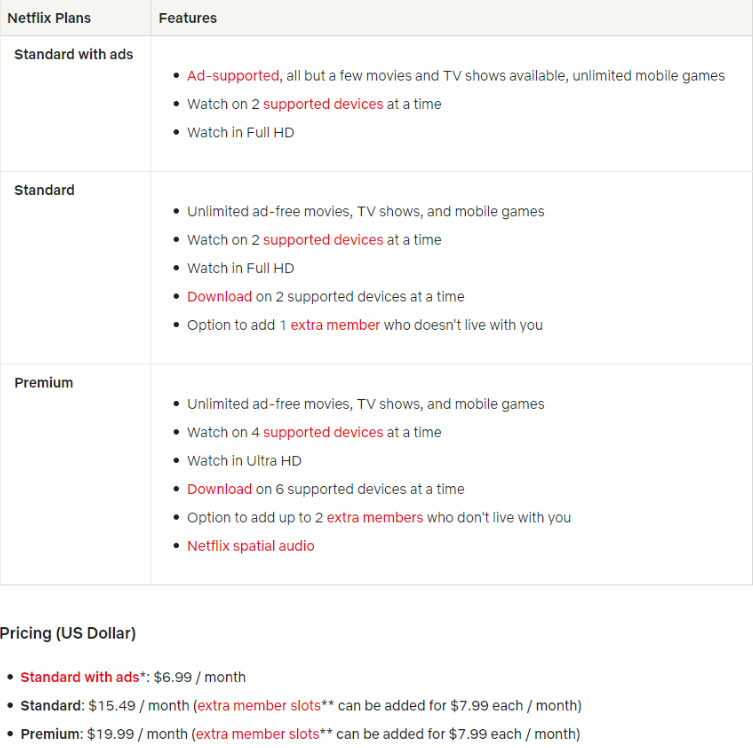
Netflix is an example of a business that uses duration-based tiered pricing. They offer multiple tiers based on the number of streams and HD/4K video quality.
Volume-Based Pricing
Volume-based pricing offers discounts when customers purchase multiple units of the same product or service. This is similar to usage-based pricing, but it’s based on the number of units purchased rather than the amount used.
For example, if you sell a product in bulk, you could create tiers based on the number of units purchased. This allows customers to choose a tier that fits their budget and needs best.
Amazon is an example of a business that uses volume-based tiered pricing. They offer discounts when customers purchase multiple units of the same product or service.
Benefits of Tiered Pricing
There are many benefits of tiered pricing, including:
- It allows businesses to offer different options at different price points and cater to a wider audience.
- It helps maximize profits by encouraging customers to opt for higher-value tiers.
- It increases customer loyalty by allowing them to choose the tier that best fits their needs.
- It simplifies the pricing structure and allows customers to easily find the tier that works best for them.
- It helps businesses stay competitive by offering more value for their customers.
Best Practice for Tiered Pricing
When implementing tiered pricing, it’s important to keep the following best practices in mind:
- Understand your customer needs and choose appropriate tiers.
- Keep the tiers simple and easy to understand.
- Provide clear information about each tier so customers can easily compare them.
- Offer incentives for customers who choose higher tiers.
- Make sure the customer experience is consistent across all tiers.
- Test different pricing strategies to determine which one works best for your business.
Final Words
Tiered pricing can be a great way to increase customer loyalty and maximize profits. By understanding how to use them, companies can create tiers that meet their customers’ needs and budgets without compromising on quality. To ensure success, it’s important to keep the best practices in mind and test different marketing strategies to determine which one works best for your business.
Featured Image Credit: Provided by the Author; Thank you!
Source link




